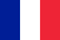
What is the knee joint?
- the joint itself;
- muscle;
- kneecap;
- meniscus;
- joint capsule;
- the ends of the femur and tibia,
- vessel,
- nerve,
- ligament
causes of joint pain
Let's look at the main causes of pain.
pain from injury
- Bruised knees.Frequent and minor damage. Swelling, redness, and increased surface temperature occur in the knee area. Even a minor injury to the knee can cause destruction of joint tissue cells.
- sprain.Sometimes a muscle, ligament or tendon sprain can go unnoticed, causing sudden and severe pain in the knee, and the joint itself can become unstable when the leg is stepped on.
- Ligament rupture.It may occur due to strong twisting of the leg in an unnatural direction and cause severe pain, swelling, and swelling.
- Meniscal tear.Occurs due to heavy loads, blows to the knees, twisting of the legs and their unnatural position. A torn meniscus can cause your legs to stop moving normally. It often occurs in athletes and is associated with swelling, bleeding, and the inability to bend the leg. There's a rule about exercise: Your knees may hurt, but they'll be gone the next morning after training. If the disease does not disappear, you need to consult a doctor.
- Joint fractures.As a result of the fracture, the soft tissue is also damaged, causing severe pain and deformation of the knee.
knee joint disease
- arthritisIt is an inflammatory process that occurs after trauma caused by infection or metabolic problems. If left untreated, the cartilage in your knee joint will continue to gradually wear away, leading to increased pain.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis– An autoimmune disease in which the body’s defense cells negatively affect tissues. The joints lose mobility, become swollen, have persistent pain, and experience increased stiffness.
- Rheumatism– In general, teenagers and those who have recently had strep throat are susceptible to infection. It is characterized by alternating unpleasant sensations.
- Arthropathy (arthrosis) of the knee.It occurs on one or both knees. The disease is characterized by a degenerative dystrophic process accompanied by the growth of connective and bone tissue that interferes with movement. In the early stages of the disease, discomfort only begins after long walks, but as the disease progresses, pain begins to occur even when walking short distances. Difficulty standing up from a chair, squatting, or walking up stairs. The pain only bothers you when you are resting. The cartilage shock-absorbing tissue is destroyed or thinned. As knee arthrosis progresses, people will notice a tightness in the knees and deformation of the joints.
- reactive arthritis– Starts a few days after intestinal infection. Severe pain combined with swelling and redness of the skin of your right or left knee usually indicates reactive arthritis.
- Bursitis– Inflammation of the joint capsule, causing severe pain and discomfort during movement.
- periarthritis– Inflammation of the tendons, muscles and ligaments around the knee joint. Pain will occur as the load on the bent leg increases.
- rickets– The cartilage that surrounds the knee joint and cushions friction and impact is destroyed.
- tumor– When they occur, blood vessels become compressed and the joint capsule deforms, causing pain and limiting mobility.
- osteoporosis– Tissues weaken, become more fragile, and the calcium content in the bones gradually decreases.
- osteomyelitis– Inflammation of bone tissue in the affected area, accompanied by swelling, fever and acute severe pain.
- Osteoarthritis– Inflammation of the joint capsule gradually becomes localized to the bone. The cartilage wears away and becomes thinner, causing the bones to no longer slide easily when moving the limb. Soreness occurs.
- Osteoarthritis– A disease that affects all parts of the joints.
- patellofemoral pain syndrome– Frequently occurs in young patients. During physical activity, the kneecap moves forward. This happens because the foot is not positioned correctly and the muscles are not prepared to bear excessive and heavy loads.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease– Knee pain when bending, climbing stairs, squatting.
- Nerve damage and neurological tissue diseases.Severe pain, numbness and tingling in the lower limbs, and difficulty in moving occur. Nerve compression occurs due to inflammation, tumors, or previous injury. Or neuritis—inflammation of nerves in one or more areas—can occur. Feel severe pain, reduced mobility and sensitivity, and involuntary contraction of the limbs.
- Impaired blood supply.
- Various other infectious diseases.Complications that develop can lead to the onset of weakness and pain.
Diagnosis of knee pain
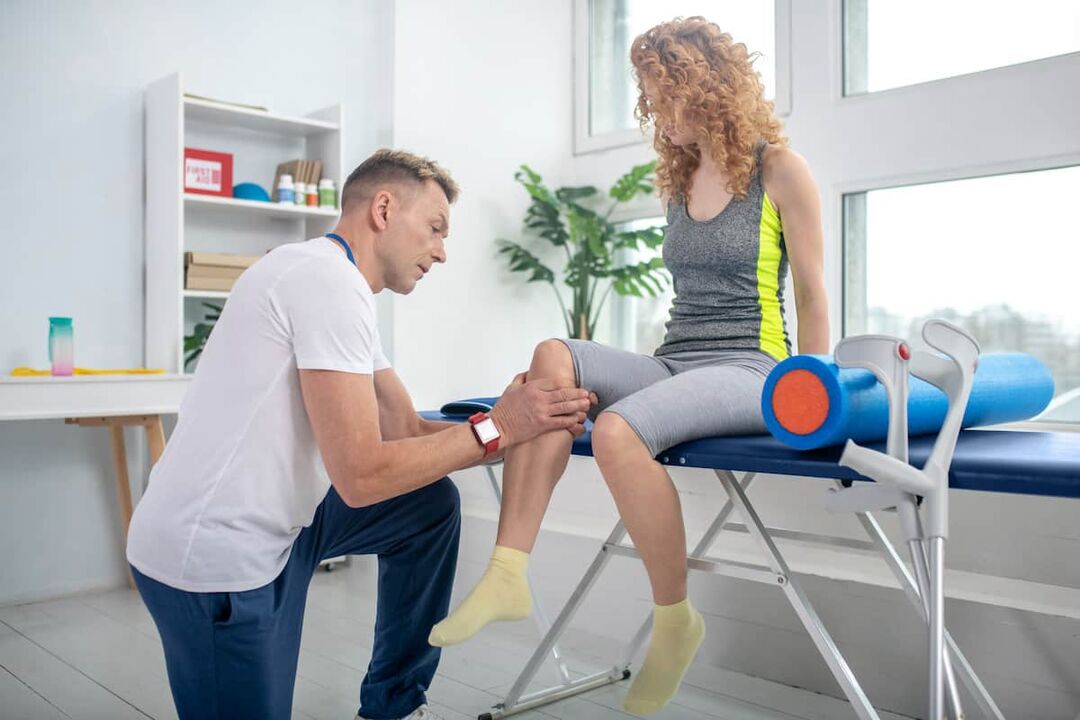

- Radiography (X-ray);
- Ultrasound (ultrasound);
- Magnetic resonance therapy (MRI);
- Computed tomography (CT);
- Arthroscopy (a special instrument, called an endoscope, is inserted into the joint);
- Puncture to collect synovial fluid;
- Laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood tests, serological tests).
Treat knee pain
- Medicinal (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or chondroprotectants - their effect is to maintain the moisture of cartilage cells, inhibit enzymatic action and prevent degenerative processes);
- Preparations and solutions for external use;
- osteopathy;
- Perform special exercises and gymnastics, physical therapy;
- physical therapy techniques;
- massage;
- Vitamin complexes are drugs used to improve metabolic processes in the body.